

Next: 2.3 CLFST...
Up: 2 Instruments and techniques...
Previous: 2.1 Cosmic Anisotropy Telescope...
2.2 Ryle Telescope
The RT is used almost exclusively for CMB work. A significant fraction of the
time is spent surveying and monitoring fields being observed by the CAT.
We have developed the rastering schemes used for this large-area mapping, and
have now implemented a scheme which gives optimally-smooth sensitivity coverage
to a noise level of 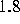 mJy over a
mJy over a 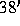 -square field in 12 hours. The
reduction procedure for these large data sets is now substantially automated.
The remainder of the RT time is mostly used for Sunyaev-Zel'dovich imaging (see
Section 1.1.3), with the unavoidable gaps in the
schedule being filled with flux-monitoring of variable galactic sources (see
Section 1.2.4).
-square field in 12 hours. The
reduction procedure for these large data sets is now substantially automated.
The remainder of the RT time is mostly used for Sunyaev-Zel'dovich imaging (see
Section 1.1.3), with the unavoidable gaps in the
schedule being filled with flux-monitoring of variable galactic sources (see
Section 1.2.4).
During the period of this report the programme of upgrading the RT cryostats
has been completed. The five antennas of the compact array now have system
temperatures of 65 K, compared with 75 K before modifications to the thermal
break, matching units and second-stage amplifiers. This results in a 30 per
cent reduction in the time required to reach a given sensitivity level. The
archiving procedures for RT data have also been improved, with a CD-ROM system
currently running alongside the Exabyte archiving.
WWW Admin Account
Mon Jun 16 17:33:05 BST 1997
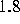 mJy over a
mJy over a 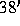 -square field in 12 hours. The
reduction procedure for these large data sets is now substantially automated.
The remainder of the RT time is mostly used for Sunyaev-Zel'dovich imaging (see
Section 1.1.3), with the unavoidable gaps in the
schedule being filled with flux-monitoring of variable galactic sources (see
Section 1.2.4).
-square field in 12 hours. The
reduction procedure for these large data sets is now substantially automated.
The remainder of the RT time is mostly used for Sunyaev-Zel'dovich imaging (see
Section 1.1.3), with the unavoidable gaps in the
schedule being filled with flux-monitoring of variable galactic sources (see
Section 1.2.4).